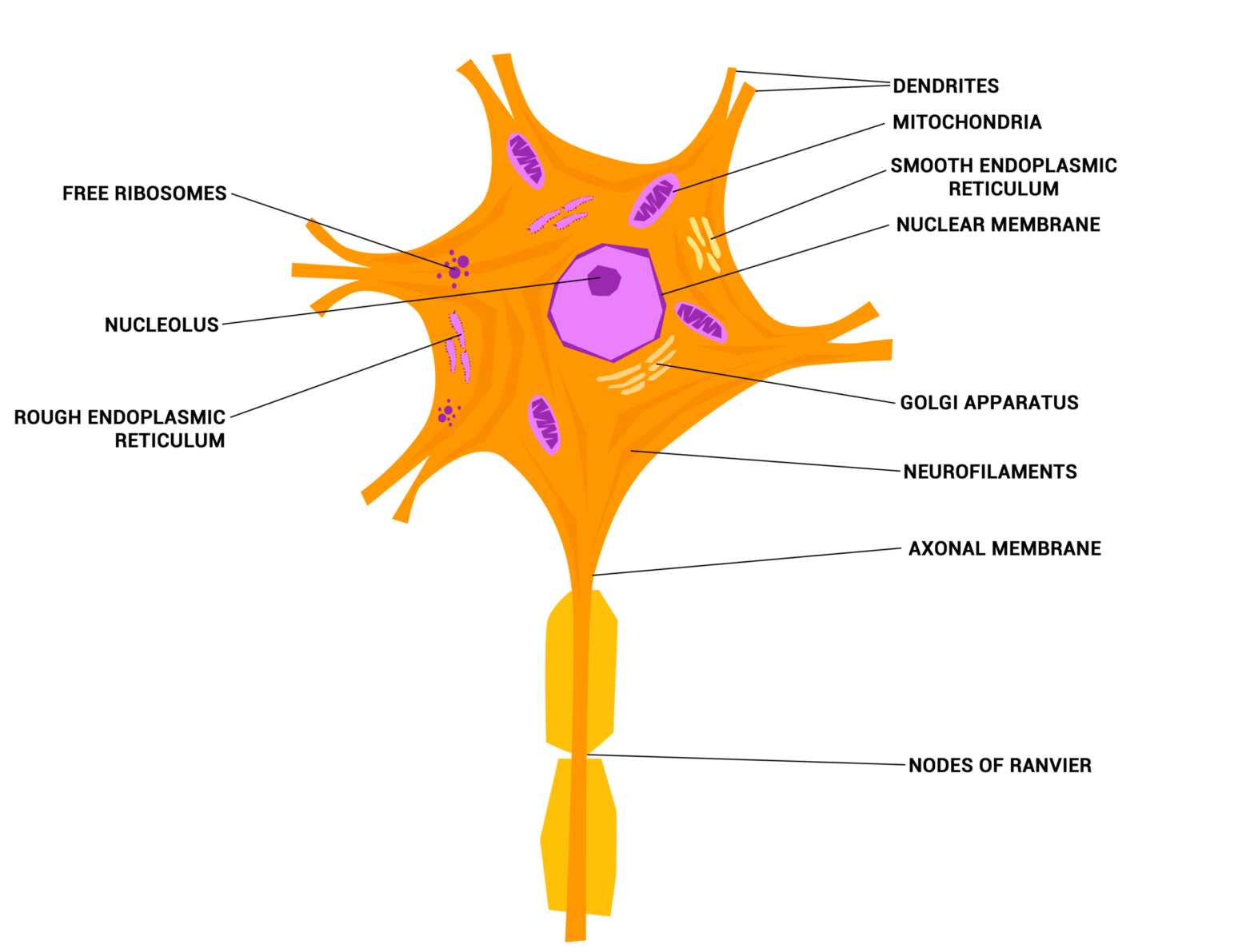
Understanding Pain: A Breakdown of Nerve Impulse Voltage
Pain is a complex sensation that serves as a warning signal, alerting us to potential harm or injury. It’s a result of electrical signals transmitted through our nervous system.
In this article, we’ll explore the physiology of pain, delve into the concept of nerve impulse voltage, and discuss five research studies that have shed light on this fascinating topic.
The Physiology of Pain
When we experience pain, it’s a result of a series of events:
- Nociception: Specialized nerve cells called nociceptors detect harmful stimuli, such as heat, cold, pressure, or chemicals.
- Transduction: Nociceptors convert the harmful stimuli into electrical signals.
- Transmission: These electrical signals travel along sensory nerves to the spinal cord and brain.
- Modulation: The brain processes these signals, interpreting them as pain.
Nerve Impulse Voltage
Nerve impulses are electrical signals that travel along nerve fibers. The strength of a nerve impulse is measured in volts. A stronger nerve impulse means a more intense pain sensation.
Several factors can influence nerve impulse voltage:
- Intensity of the stimulus: A more intense stimulus, such as a severe burn, will generate a stronger nerve impulse.
- Type of stimulus: Different types of stimuli (e.g., heat, cold, pressure) may trigger different types of nerve fibers and produce varying nerve impulse voltages.
- Nerve sensitivity: The sensitivity of the nerve fibers can also affect the strength of nerve impulses.
- Central nervous system factors: The brain and spinal cord can modulate pain signals, influencing the perceived intensity of pain.
Research Studies on Nerve Impulse Voltage and Pain
- Study on Chronic Pain: Researchers found that individuals with chronic pain often exhibit increased nerve sensitivity, leading to heightened nerve impulse voltages and persistent pain.
- Study on Opioids: A study examined the effects of opioids on nerve impulse voltage. Results showed that opioids can reduce nerve impulse voltage, leading to pain relief.
- Study on Neuropathic Pain: Researchers investigated the role of nerve damage in neuropathic pain. They discovered that damaged nerves can generate abnormal nerve impulses, contributing to persistent pain.
- Study on Phantom Limb Pain: A study explored the phenomenon of phantom limb pain, where individuals who have lost a limb continue to experience pain in the missing part. Researchers found that abnormal nerve activity in the brain can create phantom sensations, including pain.
- Study on Stress and Pain: A study examined the relationship between stress and pain. Results suggested that chronic stress can increase the sensitivity of nerve fibers, leading to heightened pain perception.
Conclusion
Understanding the physiology of pain and the role of nerve impulse voltage is crucial for developing effective pain management strategies.
By exploring research findings and gaining insights into the mechanisms of pain, we can continue to advance our knowledge and develop innovative treatments for individuals suffering from chronic pain.