Diabetes Food Plate: Master Your Meals for Balanced Blood Sugar
Are you struggling with diabetes meal planning? Discover the perfect diabetes food plate method! The diabetes food plate approach will show you how to balance carbs, proteins, and fats… and manage your blood sugar effectively. Read on to learn more!
Have you ever felt uncertain as you stare at your food, wondering if each bite will send your blood sugar spiraling out of control. That constant anxiety, the endless calculations, the feeling of being trapped by your diabetes—is exhausting.
If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed by the complexities of diabetes meal planning, you’re not alone. But what if I told you there’s a simple, visual tool that can transform your relationship with food and empower you to take control of your blood sugar?
Enter the diabetes food plate, a revolutionary approach that cuts through the confusion and provides a balanced, manageable path to healthy eating. This isn’t just another diet fad; it’s a practical, sustainable method that simplifies portion control, promotes nutrient-rich choices, and ultimately, helps you achieve stable blood sugar levels. The diabetes food plate provides a visual, balanced approach to meal planning, promoting stable blood sugar and overall health.
Table of Contents
What is the Diabetes Food Plate?
The diabetes food plate isn’t just a trendy diet; it’s a visual, practical approach to managing blood sugar through balanced meals. Imagine your plate as a canvas for healthy eating, divided into distinct sections. Each section represents a crucial component of a well-rounded diet.
The diabetes food plate method empowers you to take control of your food choices, simplifying the complex world of nutrition into a manageable, everyday practice. Let’s break down the components of this powerful tool.
Explanation of the sections of the Diabetes Food Plate
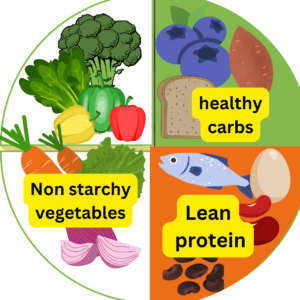
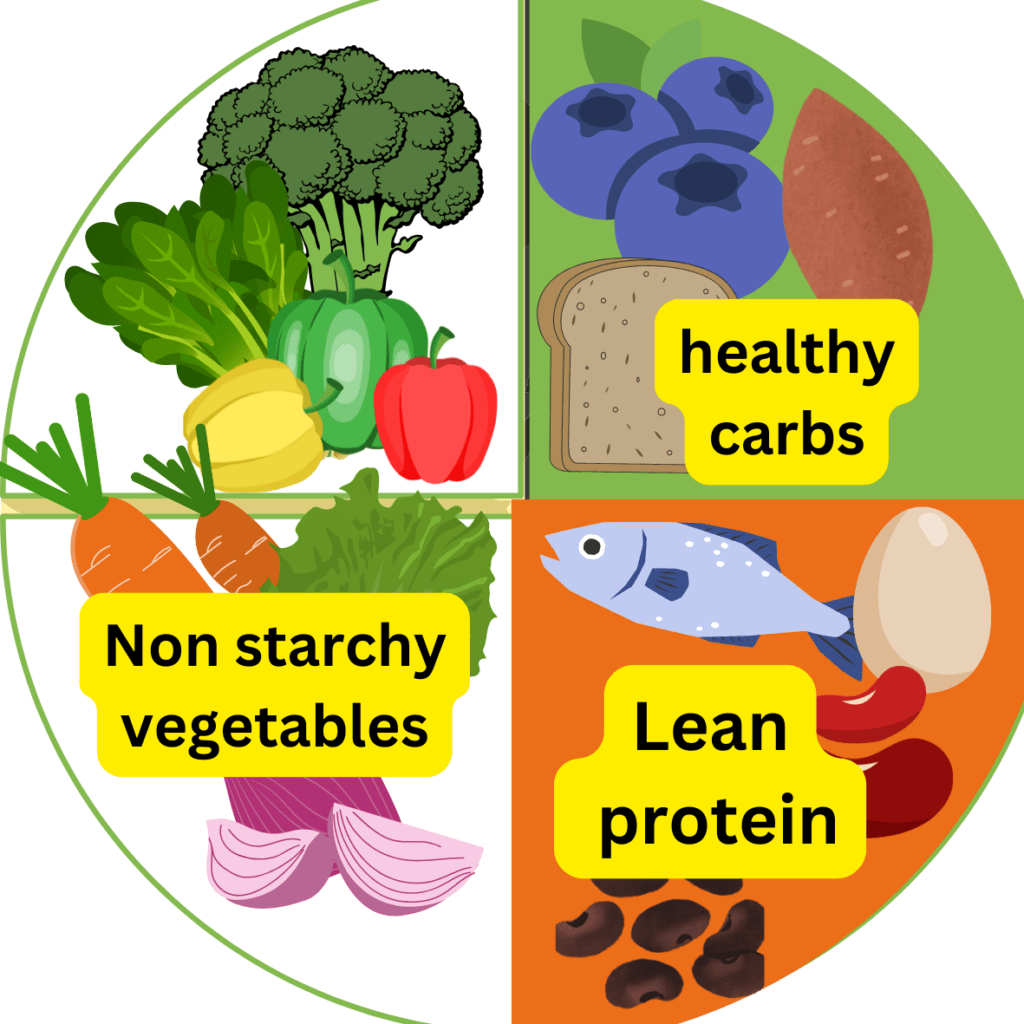
The foundation of the diabetes food plate is its simple division:.
- Half of your plate should be filled with non-starchy vegetables,
- a quarter with lean protein,
- and the remaining quarter with healthy carbohydrates.
This visual guide allows for quick and easy meal assembly, eliminating the need for complex calculations or rigid meal plans. By adhering to these proportions, individuals can ensure they are consuming a balanced intake of essential nutrients, promoting stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
This visual representation helps to promote portion control. Many people struggle with overeating, and the plate method provides a clear visual cue for appropriate serving sizes. Additionally, the plate method can be adapted to fit various dietary needs and preferences, making it a versatile tool for individuals with diabetes.

Breakdown of the sections of the diabetes food plate
Non-starchy vegetables (half plate):
These are the cornerstone of the diabetes food plate. Non-starchy vegetables offer a wealth of vitamins, minerals, and fiber without significantly impacting blood sugar levels.
Non-starchy vegetables include:
- leafy greens like spinach and kale,
- cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower,
- and vibrant options like bell peppers (all colors), asparagus, green beans and cucumbers.
Filling half of your plate with these nutrient-rich foods provides essential nutrients and promotes satiety, helping you feel full and satisfied after meals.
Fiber is a very important part of the non-starchy vegetable group. Fiber slows down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, helping to prevent blood sugar spikes. It also promotes healthy digestion and can contribute to weight management. Furthermore, the variety of colors and textures in non-starchy vegetables adds interest and enjoyment to meals, making healthy eating a more pleasurable experience.
Lean protein (quarter plate):
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and promoting satiety. Lean protein sources , provide these benefits without adding excessive saturated fat. Sources of lean protein include:
- skinless chicken breast,
- skinless turkey breast
- fish like tuna, salmon and cod.
- tempeh
- tofu,
- beans
- tempeh
- lean ground beef (90% lean or higher)
- Eggs (in moderation)
- Greek yogurt (plain, non-fat)
- Beans (black beans, kidney beans)
- Lentils
Include a quarter plate of lean protein in your meals to stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates.
Protein also helps to preserve muscle mass, which is particularly important for individuals with diabetes. Maintaining muscle mass can improve insulin sensitivity and support overall metabolic health. Choosing a variety of lean protein sources ensures that you are obtaining a diverse range of amino acids, the building blocks of protein, which are essential for optimal health.
Healthy carbohydrates (quarter plate):
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. It is important to choose the right types to manage blood sugar. Healthy carbohydrates are also called complex carbohydrates. They provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber. They help to regulate blood sugar levels.
Healthy carbohydrate options include:
- whole grains like brown rice and quinoa, rolled or steel cut oats, whole wheat bread, whole grain pasta
- legumes like lentils and chickpeas,
- starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes, yams, eddoes, dasheens and corn.
- berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
It is important to pay close attention to portion sizes when consuming carbohydrates, as they have the most direct impact on blood glucose. Opting for complex carbohydrates over refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and sugary drinks, is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar. Complex carbohydrates are digested more slowly, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose.
The Diabetes Food Plate is a visual meal-planning tool that simplifies healthy eating for people with diabetes. It divides your plate into three sections: half for non-starchy vegetables, a quarter for lean protein, and a quarter for healthy carbohydrates. This visual guide helps with portion control and ensures a balanced intake of essential nutrients, promoting stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
Benefits of Using the Diabetes Food Plate
The diabetes food plate offers a multitude of benefits, extending far beyond simple meal planning. It’s a tool that empowers individuals to take control of their health, promoting stable blood sugar levels, weight management, and overall well-being. By adopting this method, individuals can experience a significant improvement in their quality of life. Let’s delve into the specific advantages of using the diabetes food plate.
Improved blood sugar management
The balanced proportions of the diabetes food plate help to regulate the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing drastic spikes and dips in blood sugar levels. By consistently adhering to the plate method, individuals can achieve more stable blood glucose readings throughout the day, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
This stable blood sugar management helps to prevent long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular problems. Consistently managing blood sugars allows those with diabetes to feel better daily, and have more energy.
Weight management support
The diabetes food plate promotes portion control and encourages the consumption of nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods, which are essential for weight management. By filling half of the plate with non-starchy vegetables, individuals can feel full and satisfied without consuming excessive calories. The balance of protein and carbohydrates also contributes to satiety, helping to prevent overeating.
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as excess weight can exacerbate insulin resistance and increase the risk of complications. The diabetes food plate provides a sustainable approach to weight management, promoting gradual and consistent weight loss or maintenance.
Simplified meal planning
The visual nature of the diabetes food plate eliminates the need for complex calculations or rigid meal plans, making meal planning quick and easy. By simply dividing your plate into the appropriate sections, you can create balanced and nutritious meals without feeling overwhelmed. This simplicity makes the plate method a practical and sustainable approach to healthy eating.
This simplified approach to meal planning can reduce stress and anxiety associated with food choices, making healthy eating a more enjoyable and manageable experience. It also allows for greater flexibility, enabling individuals to adapt the plate method to their personal preferences and dietary needs.
Increased nutrient intake
The emphasis on non-starchy vegetables, lean protein, and healthy carbohydrates ensures that individuals are consuming a wide range of essential nutrients. These nutrients support various bodily functions, including immune function, energy production, and cell repair. By prioritizing nutrient-rich foods, individuals can optimize their overall health and well-being.
Consuming a variety of colorful non-starchy vegetables will increase vitamin and mineral intake. Variety in protein sources will help to ensure all essential amino acids are consumed. Choosing whole grains and other complex carbohydrates increases fiber intake.
sing the Diabetes Food Plate offers numerous benefits, including improved blood sugar management, weight management support, simplified meal planning, and increased nutrient intake. By adopting this method, individuals with diabetes can experience better blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life.
Choosing the Right Foods for Your Plate
The Diabetes Food Plate isn’t just about proportions; it’s about making mindful choices within each section. Let’s explore some ideal food options for each part of your plate:
Non-starchy vegetables:
The possibilities here are endless! Think leafy greens like spinach and kale, cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower, vibrant bell peppers, cucumbers, and zucchini. Aim for a variety of colors to maximize nutrient intake.
Tips for preparing non-starchy vegetables
- Steaming, grilling, or roasting are healthy cooking methods that preserve nutrients.
Salads are a fantastic way to incorporate a large volume of non-starchy vegetables into your meals.
Add them to soups, stir-fries, and omelets for a nutrient boost.
Lean protein in the Diabetes food plate
This section emphasizes protein sources that are low in saturated fat. Excellent choices include:
- Poultry: Chicken (skinless), turkey-
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, cod
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas
- Tofu and tempeh (for vegetarian/vegan options)
- Eggs: In moderation
- Lean cuts of beef – choose lean cuts and trim visible fat.
Tips for preparing lean protein
- Grill, bake, or poach protein for healthier cooking methods.
- Limit processed meats such as sausages and bacon
Healthy or complex carbohydrates in the diabetes food plate
This section focuses on carbohydrate sources that provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber. Focus on
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole-wheat bread, whole-grain pasta
- Starchy vegetables: Sweet potatoes, yams, dasheens, eddoes, cassava, corn, peas (in moderation)
- Fruits: Berries, apples, oranges, bananas (in moderation due to their natural sugar content)
Tips for healthy or complex carbohydrates on your plate:
- Choose whole grains over refined grains whenever possible.
- Be mindful of portion sizes, as starchy vegetables and fruits contain natural sugars.
- Combine carbohydrates with protein and fiber to slow down sugar absorption.
Choosing the right foods for your Diabetes Food Plate is crucial. Non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and peppers should fill half your plate. Lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, tofu, and beans should occupy a quarter, while healthy carbohydrates like whole grains, starchy vegetables, and fruits should make up the remaining quarter.
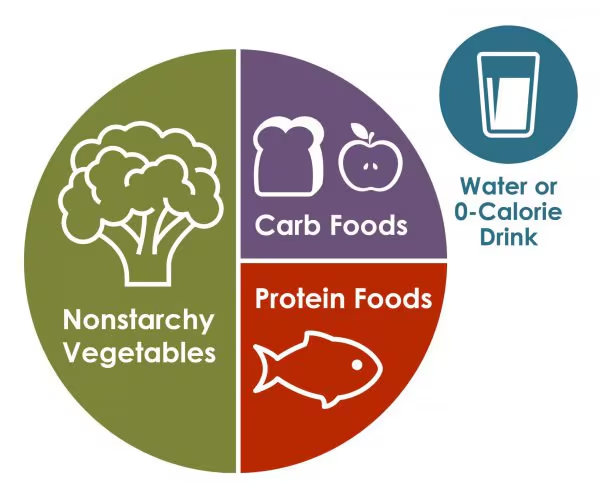
Zero Calorie Drinks
Your meals should also include zero calorie drinks to prevent glucose spikes. Examples include:
Staying hydrated with zero-calorie beverages is crucial, especially for those managing diabetes. Here’s a list of 6 refreshing and healthy options:
Hydrating Zero-Calorie Drinks
These beverages provide essential hydration without impacting blood sugar levels, making them ideal choices for a diabetes-friendly diet.
1. Water: The ultimate zero-calorie hydrator. Plain water is essential for all bodily functions.
2. Sparkling Water: A fizzy and refreshing alternative to plain water. You can find many naturally flavored versions.
3. Unsweetened Tea (Hot or Iced): Herbal teas (chamomile, peppermint, hibiscus) and traditional teas (green, black) without added sugar are excellent choices.
4. Infused Water: Add slices of cucumber, lemon, lime, or berries to water for a flavorful and refreshing drink.
5. Unsweetened Iced Tea: Brew your own tea and chill it for a refreshing drink. Avoid pre-made iced teas that often contain added sugars.
6.. Water with Apple cider vinegar: A small amount of apple cider vinegar added to water can be a healthy addition to a diet.
.Important Considerations:
- While diet sodas and artificially sweetened beverages are zero-calorie, some studies suggest they may still impact health. It’s best to consume them in moderation or not at all.
- It is always a good idea to check with a doctor or nutritionist, for personalized diet advice.

Portion Control and the Diabetes Food Plate
The Diabetes Food Plate emphasizes not only what you eat but also how much you eat. Portion control is crucial for managing blood sugar and maintaining a healthy weight. Here are some tips:
Visual cues: Use your hands as a guide. A portion of protein is about the size of your palm. A serving of non-starchy vegetables is roughly the size of your fist.
Measuring tools: Utilize measuring cups and spoons for accurate portion sizes, especially for carbohydrates.
Read food labels: Pay attention to serving sizes and nutrient content.
Practice mindful eating: Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Eat slowly and savor each bite.
Avoid distractions: Minimize distractions while eating, such as TV or phones, to focus on your meal.
Portion control is essential when using the Diabetes Food Plate. Visual cues, measuring tools, and mindful eating practices can help you manage your food intake effectively. Working with a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on portion sizes and calorie requirements based on your individual needs and health goals.
Diabetes Food Plate Caloric Requirements
Caloric needs vary significantly from person to person based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and weight goals. The Diabetes Food Plate doesn’t specify a strict calorie count, but it provides a framework for creating balanced meals that support your individual needs.
Work with a registered dietitian: A registered dietitian can help you determine your individual calorie needs and create a personalized meal plan based on your specific health goals.
Consider your activity level: If you’re more active, you’ll likely need more calories.
Monitor your weight: Track your weight regularly to ensure you’re maintaining a healthy weight range.
Remember: The Diabetes Food Plate is a flexible guide, not a rigid set of rules. It’s about making conscious choices and creating a sustainable eating pattern that supports your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
The Diabetes Food Plate is a powerful and adaptable tool for managing diabetes through healthy eating. By understanding the plate’s sections, choosing the right foods, and practicing portion control, individuals with diabetes can take control of their blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and improve their overall well-being.
Remember, the Diabetes Food Plate is a flexible guide, not a rigid set of rules. It’s about making informed choices and creating a sustainable eating pattern that supports your health and happiness.
Sources
American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Diabetes Plate Method. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/recipes-nutrition/eating-well/diabetes-plate-method
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Managing Diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/index.html
Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/diabetes-diet/art-20044295
U.S. Department of Agriculture. (n.d.). MyPlate. Retrieved from https://www.myplate.gov/